Ovarian Cancer - Symptoms and Treatment - Avicenna Health
Ovarian Cancer
Do you feel continuously bloated?
Do you have a swollen tummy?
Do you get any discomfort in the tummy or pelvic area?
Or do you feel full quickly when eating?
Do you need to pee more frequently than usual?
Definition of the illness:
Ovarian cancer, or cancer of the ovaries, is one of the most common cancers in females.
The ovaries are a couple of small organs located low in the tummy linked to the womb and save a woman's supply of eggs.
Ovarian cancer mainly influences females who have been through menopause (commonly over the age of 50); however, it could occasionally affect women that are more youthful.
Symptoms:
When ovarian cancer first develops, it may not cause significant signs or symptoms. When symptoms of ovarian cancer do occur, they are usually attributed to other, more common conditions.
The signs and symptoms could also include:
- Flatulence or gas
- Feeling bloated when eating
- Weight loss
- Pelvic discomfort
- Fatigue
- Back pain
- Changes in bowel habits, including constipation
Causes:
It's identified what causes ovarian cancer, though doctors have determined things that may increase the possibility of the disease.
Doctors Say that ovarian cancer begins as soon as cells close to the ovaries develop changes in their DNA.
A cell's DNA include the instructions that tell the cell how to work. The changes mean the cells grow and multiply quickly, creating cancer cells' mass (tumor).
The cancer cells continue working when healthy cells would die. They could invade nearby tissues and break off from an initial neoplasm to unfold (metastasize) to different areas of the body.
Risk Factors:
Many factors that could increase the risk of getting ovarian cancer consist of:
1- Older age Inherited gene changes: The genes that increase the risk of ovarian cancer are BRCA1 and BRCA2.
2- Family background of ovarian cancer.
3- Overweight or obese.
4- Postmenopausal hormone replacement therapy.
5- Endometriosis.
6- Age when the menstrual period starts and ends: Beginning earlier or starting menopause at a later age, or both, may also increase the risk.
7- Never having been pregnant.
When to see a doctor
Make an appointment with a physician when you have any signs or symptoms that worry you.
Diagnosis:
Tests and strategies used to diagnose ovarian cancer consist of:
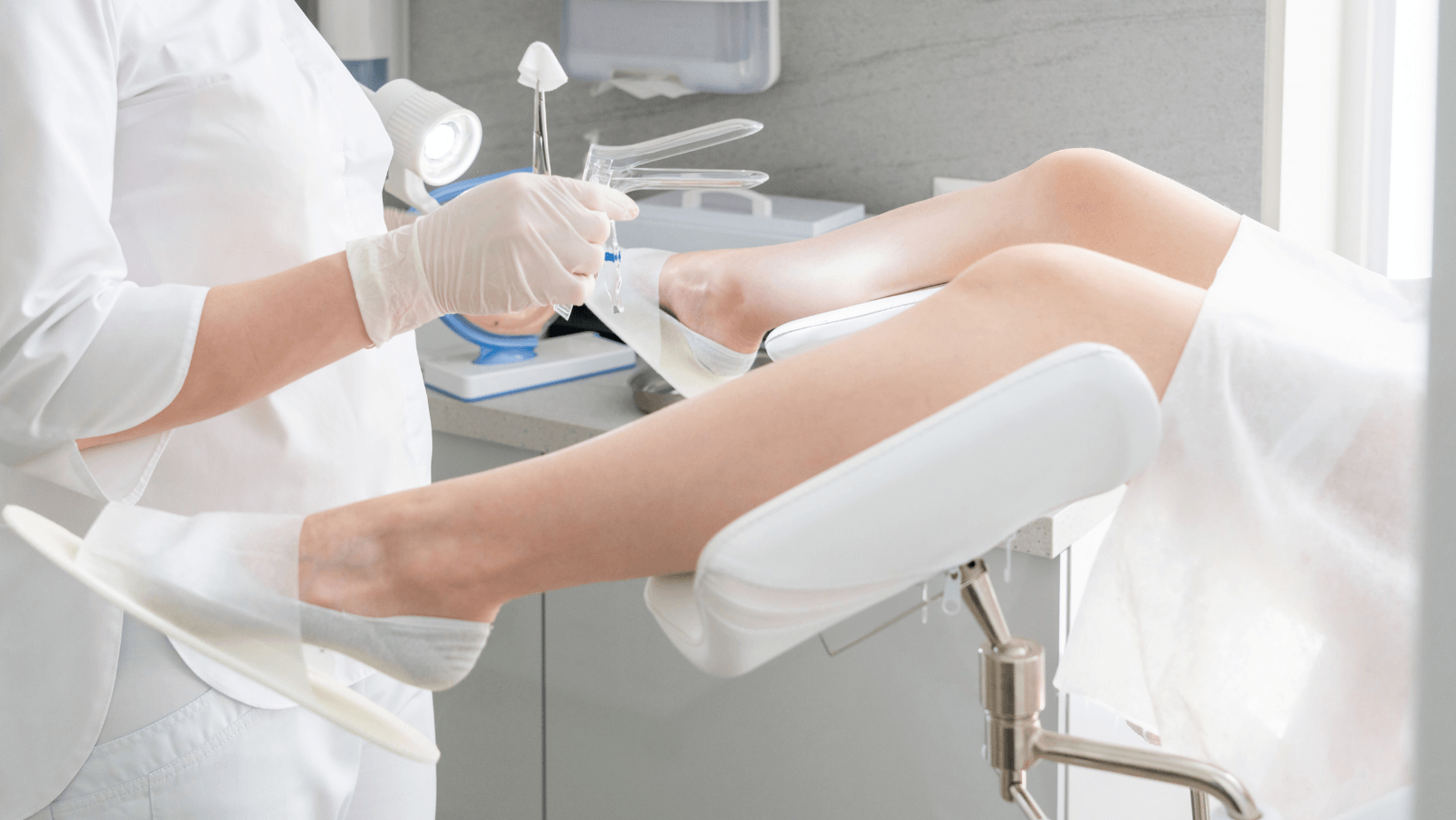
1- Pelvic exam: During a pelvic exam, your physician inserts gloved fingers into the vagina and concurrently presses a hand in Belly with the purpose to feel (palpate) pelvic organs. The physician additionally visually examines external genitalia, vagina, and cervix.
2- Imaging tests. Tests, including ultrasound or CT scans of the abdomen and pelvis, may also assist in determining the size, form, and structure of ovaries.
3- Blood tests. Blood tests may include organ function tests which can assist decide standard health.
Your physician may also check your blood for tumor markers that imply ovarian cancer. For example, a cancer antigen (CA) 125 check can discover a protein frequently located on the surface of ovarian cancer cells. These tests cannot inform a physician whether you have cancer, but they will make clues about diagnosis and prognosis.
4- Surgery: Sometimes, your physician cannot be sure of prognosis until you undergo a surgical operation to get rid of an ovary and have it examined for signs of cancer.
5- Genetic testing: Your physician may also suggest testing a blood sample to search for gene modifications that increase the danger of most ovarian cancers.
Differential Diagnosis:
- Appendiceal tumors
- Benign lesions of the uterine corpus
- Bladder distention/urinary retention
- Bowel omental adhesions
- Colon cancer
- Embryologic remnants
- Fecal impaction
- Gastric adenocarcinoma
- Low-lying cecum
- Metastatic gastrointestinal carcinoma
- Ovarian torsion
- Pelvic abscess
- Pelvic kidney
- Peritoneal cyst
- Retroperitoneal mass
- Urachal cyst
- Uterine anomalies
- Uterine fibroids
Management:
The treatment relies upon how far it has spread, your general health, and whether you are still capable of having babies. Most people have a mixture of both surgical and chemical treatment. Surgery is the principal treatment. The purpose is to get rid of all cancer, or as much of it as possible.
1- Surgical treatment usually includes removing:
- ovaries
- the fallopian tubes
- metrectomy
- a layer of fatty tissue inside the tummy
2- Chemotherapy is where medication is used to kill cancer cells. Most females with ovarian cancer have chemotherapy similar to surgery.
3- Radiotherapy: Radiotherapy uses cautiously directed beams of radiation to kill cancer cells.
4- Targeted therapies: Targeted therapies are drugs that change the way cells work and stop cancer from developing and spreading. Not all kinds of ovarian cancer may be handled with targeted therapies.
References:
- Mayoclinic
- NCBI
- Medscape